First Prize: Rachel Lacroix
PhD Candidate
Lab: Dr. Deborah Kurrasch
Summary: In the brain, axons (nerve fibers) transmit electrical impulses between neurons, allowing neural information to travel and be synthesized by other areas of the brain. This image shows axons (orange) and cell nuclei (blue) of a whole zebrafish brain, a pattern which may be altered by genetic or environmental insults, indicating a neurodevelopmental disturbance.

Second Prize: Jordan Lee
Postdoctoral Fellow
Lab: Dr. Aaron Phillips
Summary: Tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) containing neurons (cells from the “fight-or-flight” nervous system) in a mouse heart. TH neurons are essential for fine-tuned, dynamic control of the heart’s pumping ability. Studying how TH neurons change in disease states will inform development of therapies for heart disease.

Third Prize: Rianne Gorter
Postdoctoral Fellow
Lab: Dr. VW Yong
Summary: This is a slice of mouse cerebellum or ‘little brain’. The orange lines are nerve cell processes through which electrical signals are transmitted. The blue surrounding these orange cables is myelin, an insulating layer, which ensures that nerve signals can travel at superspeed. This enables coordinated movements, just like in humans.

Fourth Prize: James Sousa
Masters Student
Lab: Dr. Maitreyi Raman and Dr. Derek McKay
Summary: Mouse colon section stained with an oxidation sensitive probe to study oxidative stress in tissue. The probe stains lipids and lipid membranes. Lipids peroxides also oxidize the probe which results in a change in fluorescence (indicated by yellow to red). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue).
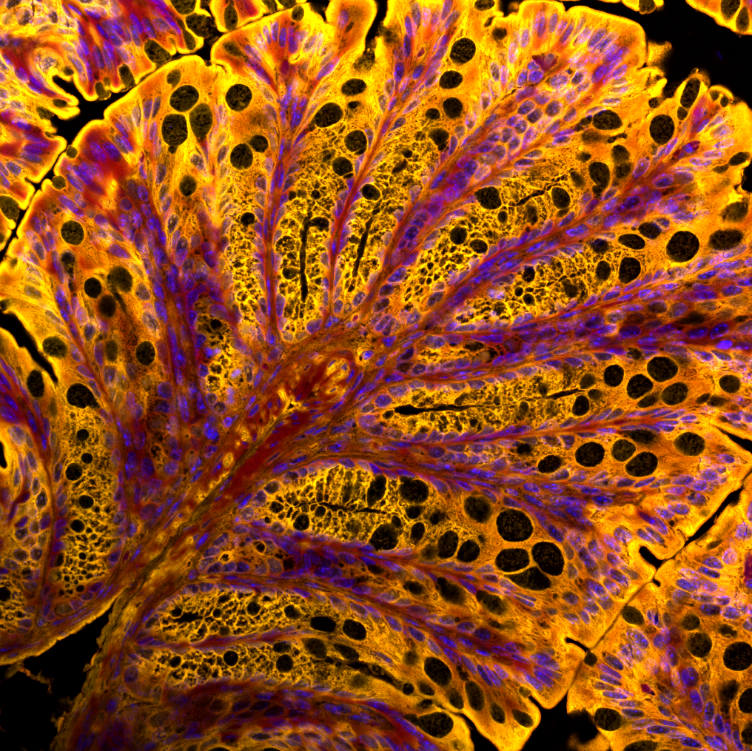
Fifth Prize: Qianqian Guo
Postdoctorate Fellow
Lab: Dr. Jiami Guo
Summary: Purkinje cells & Pre-synapses. The images shows Purkinje cells (magenta) and pre-synapses (yellow) in mouse cerebellum. Nuclei are shown in cyan.

Fifth Prize: Richard Yu
PhD Student
Lab: Dr. Aaron Phillips
Summary: This is a brainstem taken from an adult mouse chemically processed to render the specimen mostly transparent (hence called "clearing") to facilitate imaging of the whole sample using an advanced microscope called lightsheet microscope. The specimen is stained for the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase, which is a marker of a branch of autonomic nervous system important for the regulation of cardiovascular function.



